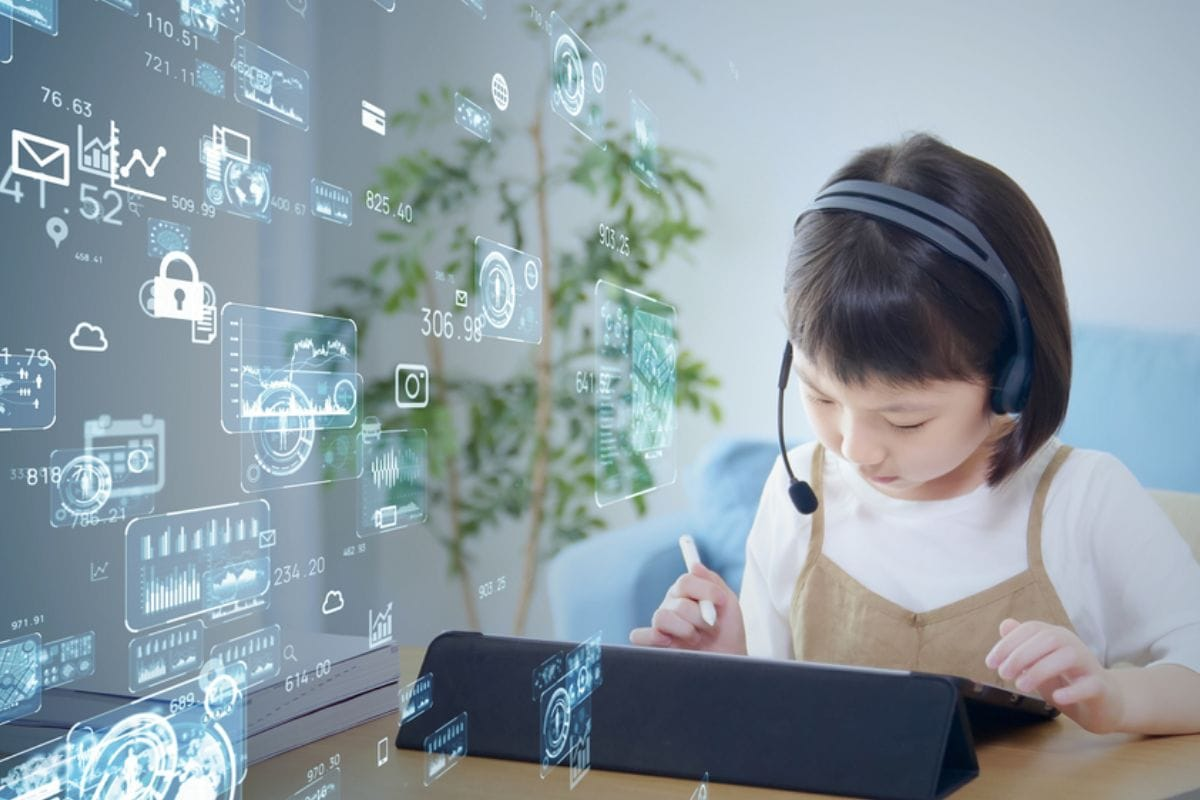
In a big step towards accessible and child-safe technology, Google is planning to roll out its Chatbot for under 13 years user, aiming to make Artificial Intelligence more inclusive for young users. The step is part of Google’s broad strategy, where educational, age -appointed and safely monitored, to introduce artificial intelligence equipment.
This development opens the door to a new era of child-safe AI that promises to educate, entertain, and strengthen children while maintaining strict security and privacy standards.
Table of Contents
What Is a Chatbot for Under 13 Children?
A Chatbot for under 13 is an AI-operated intellectual accessory designed for children under the age of 13. Unlike traditional AI devices used by teens and adults, these are chatbots:
- Age-appropriate
- Privacy-compliant
- Highly monitored
- Educational in design
The version of Google is likely to be a child-friendly form of Gemini (East Bard) Chatbot, which is U.S.
Why Create Chatbots for Children?
Children already interact with voice-based tools such as Google Assistant, Alexa, and Siri. By making a dedicated Chatbot for under 13 years, Google’s goal is:
- Provide a safe place for curious brains to ask questions
- Supported interactive learning in subjects such as mathematics, science, reading, and more
- Encourage creativity through history and games
- Help children become digitally literate and responsible users of technology
Google’s child-specific chatbot will be linked to supervision of Google accounts, which will give parents full control over their child’s calls and settings.
A chatbot for the young, so safe and wise, Guiding little minds, with open skies. Learning through each chat and game, A future bright, no two days the same.
Privacy and Parental Controls
Starting a Chatbot for under 13 brings strict requirements for security and data security. Google is working to secure:
- No personal data is collected without the consent of the parents.
- The interaction is moderated to filter unsafe or incorrect content.
- Parents allow monitoring of the dashboard, limiting the use and management of permits
- Ads and profiling are fully disabled for users under 13
Parents can expect a perfectly transparent experience, with equipment, what the child sees, listens and learns through the chatbot.
Educational Applications
One of the strongest benefits of Chatbot for under 13 is its ability to improve learning outcomes. Chatbot will act as a virtual supervisor or study partner, activated:
- Explain difficult concepts in simple, age-appropriate language.
- Provide practice questions and answers in different subjects
- Inspires curiosity with fun facts, general knowledge, and history.
- Help for homework, offer signals and clarifications without responding.
By feeling learning as a natural interaction, Chatbot helps children to engage more actively with traditional study methods.
Ethical and Developmental Considerations
While the idea of giving access to AI to young children can increase concerns, experts say it is an intentional design. A Chatbot for under 13 should not only be safe, but also develop developmentally-significant thinking, healthy technical habits, and balanced screen time.
Some psychologists are carefully encouraging and reminding the parents to ensure the complement of AI tools, not compensation, human interaction, especially for many years of important development.
What’s Next?
Google planned to roll Chatbot for under 13 in steps starting in selected regions such as the United States, before expanding globally based on users’ feedback, cultural ideas and compliance with local privacy laws.
This step can soon affect other technical giants, which can lead to an entire AI for children’s ecosystems, not only for entertainment, but also with chatbots for education and emotional development.
Final Thoughts
As technology develops, the line between digital assistants and virtual teachers continues to blur. Google’s Chatbot for under 13 reflects a further thinking approach to AI, where safety, learning and responsible innovations are run by hand.
The challenge now lies in creating the right balance between innovation and inspection – young users need to grow up with devices that not only answer questions, but also inspire self -confidence, curiosity and care.